Flat Feet
Flat Feet
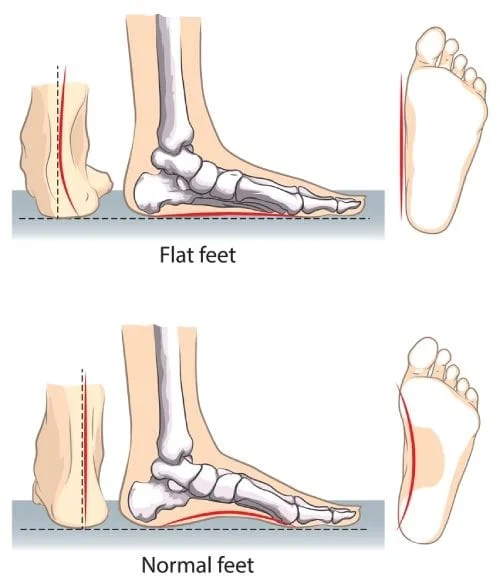
Flat feet, also known as fallen arch or pes planus, is a condition that involves having very low or non-existent arches. When babies are born, they often have flat feet that form arches as they grow. In adults with flat feet, their arches may not have developed which results in the formation of flat feet. There are cases where arches can collapse, also known as fallen arches.
There are two main types of flat feet:
- Flexible flatfoot (flexible pes planus) happens when the foot becomes flat due to bearing weight and returns to normal afterward. It is a common condition that young children have but goes away with age as arches fully form.
- Rigid flatfoot (rigid pes planus) refers to an arch being flat regardless of its position. This type of flatfoot is what causes issues.
Flat feet can cause pain in the toes, ankles, knees, hips, and lower back. The pain is brought on by the inability to support your body weight or absorb the force from movements. The weight load shifts onto other parts of your feet and lower legs, which can cause pain, discomfort, and other foot conditions.
Some of those other conditions involve the following:
- Plantar fasciitis
- Achilles tendonitis
- Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction
- Shin splints
- Hammertoes
- Bunions
- Calluses
Symptoms
What Are the Symptoms of Flat Feet?
There are cases in which flat feet are asymptomatic, but the condition can affect other parts of your body. The issues can eventually become serious and painful with age.
However, the most common symptoms associated with flat feet are:
- Foot pain
- Heel pain
- Ankle pain
- Hip pain
- Leg cramps
- Muscle pain
- Tight Achilles tendon
- Overpronation: Feet that roll inward while walking or running)
- Toe drift, in which the front part of the foot and toes start pointing outwards
When Should I See a Doctor?
It may be time to see a Podiatrist if you are dealing with the following experiences:
- Difficulty walking due to pain in the feet
- Difficulty balancing
- Sudden formation of fallen arches
- Painful stiffness in your feet
Causes
What Causes Flat Feet?
Arches begin to develop early in childhood, so there is always the risk that an adult has collapsed arches or inherited the condition, such as rigid or flexible flatfoot.
Many causes can contribute to the development of flat feet:
- Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction: The posterior tibial tendon supports the arch of your foot. The tendon can become damaged and cause the arch to collapse, leading to flat feet.
- Prolonged stress to the foot damages the ligaments and bones that keep your arches up
- High-impact injuries or trauma to the talus bone
- Tears in the posterior tibial tendon
- Faulty biomechanics that places stress and strain on your joints and muscles can create damage to bones, ligaments, and muscles
- The wear and tear of aging can add strain and damage to the posterior tibial tendon, leading to flat feet.
- An increased weight load from pregnancy or obesity can cause the collapsing of arches in the feet.
- Rheumatoid arthritis, as tendons, ligaments, and bones shift out of their regular positions and cause fallen arches.
- If you are diabetic, Charcot foot is something that may occur and result in the midfoot collapsing.
Diagnosis
How Are Flat Feet Diagnosed?
A healthcare provider can assist in diagnosing flat feet by assessing the structure of your arches when you stand, walk, run, or sit. The best way to look at the foot’s bone structure is with x-rays.
Treatment
How Can Flat Feet Be Treated?
You may want to seek treatment if you are experiencing pain while walking or standing, as well as having problems balancing.
There are various treatment options, such as:
- Custom orthotics to help support biomechanical movements and support bodyweight and distribution along the bottom of your feet. Orthotics can relieve pain or strain on your muscles or joints.
- Modified insoles are specifically designed to add comfort and support that is needed when dealing with flat feet.
- Motion control or stability shoes can assist with overpronation.
- Avoid shoes with flat soles, such as flats or flip-flops.
- Practicing foot and lower limb stretches. These stretches can help strengthen your muscles so that they can take on the extra burden of weight. They will also create more resistance in your ligaments to be more effective in holding up your arches.
- The use of shockwave therapy. This treatment involves using high-frequency energy pulses from sound waves to treat the muscles and tendons associated with flat feet.
In some cases, some lifestyle changes may be necessary to accommodate the relief of your flat foot condition. A diet or exercise program may be suggested to manage your weight gain to reduce any pressure on your feet.
Specific exercises, even walking or running, may have to be expelled to reduce the pain you may experience with flat feet.
If pain is excruciating, your doctor may prescribe nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medication to reduce inflammation or discomfort and relieve pain.
Surgical treatments are typically a last resort option, as treatment with orthotics can yield better results. Surgery complications can include infections, improper healing of bones, excessive pain, and poor ankle or foot movement.
Risk Factors
There are specific factors that may increase the risk of developing flat feet, such as:
- Flat feet can be inherited. You are more likely to be at risk of flat feet if it runs within your family.
- Overpronation can lead to muscle imbalance.
- Injury or damage to the posterior tibial tendon
- Wear and tear of the posterior tibial tendon due to age
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Pregnancy
- Weight gain
Flat feet can also lead to the development of other foot problems:
- Bone spurs
- Bunions, corns, and calluses
- Shin splints
- Pain in the lower back and lower limbs
Prevention
How Do I Prevent Flat Feet?
A flat foot condition is difficult to prevent, as it can be hereditary. However, there are some precautions you can take to reduce the risk of excessive pain:
- Wearing shoes that fit properly and provide comfort
- Custom orthotics to provide support and comfort
- Maintaining a healthy weight
Stretching
Practicing ankle stretches against resistance to strengthen the muscles in your feet and lower limbs. These stretches include:
- Eversion: Turning the sole of your foot away from your body’s midline
- Inversion: Turning the sole of your foot inward to your body’s midline
- Dorsiflexion: Lifting your foot upward to the shin
- Plantarflexion: Lifting your foot down to the calf
If you are dealing with pain and discomfort in your feet, schedule an appointment with our licenced foot specialists today. We offer many services that handle your foot needs. While you may walk in with concerns, we ensure you will be given the proper treatment plans and products available.