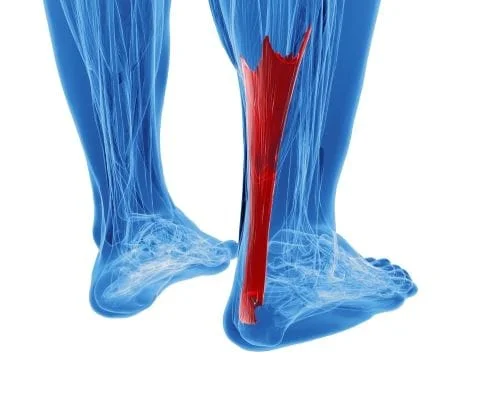
Achilles Tendonitis
Achilles Tendonitis
What Is Achilles Tendinitis?
Achilles tendinitis is a painful condition that causes irritation and inflammation in the Achilles tendon. The Achilles tendon acts as the link that attaches your calf muscles to the heel bone, or calcaneus. If you notice pain or swelling above the back of your heel, it’s probably Achilles tendinitis. As the foot condition progresses, it can become difficult to move the foot or ankle, at all.
There are two types of Achilles tendinitis:
- Insertional Achilles tendinitis affects the lower portion of the tendon that attaches to the heel bone. This type of Achilles tendinitis can affect anyone at any age, including those that aren’t physically active.
- Noninsertional Achilles tendinitis involves the formation of small tears in the fibres of the tendon. It can eventually lead to the swelling or thickening of the tendon. This type often affects younger individuals that are active, such as runners.
Over time, the pain and inflammation can worsen. With proper attention from a foot specialist, this condition can be treated.
Symptoms
The most common symptoms of Achilles tendinitis are pain and swelling in the back of your heel. You may also experience a tightness in the calf muscles or a limited range of motion as you flex your feet.
Other symptoms of Achilles tendinitis are:
- Pain in your heel when you touch or move it
- Pain in your calf muscle
- Pain or swelling that intensifies when active, such as walking, running, or jumping
- Pain or swelling in the area the day after you exercise
- Pain or swelling in the back of the heel
- Pain in the back of your heel when you wear shoes
- Bone spur formation
- Warmth around the heel/tendon
- Limited range of movement while flexing your foot
- Thickening of your Achilles tendon
- Difficulty standing on your toes
- Overall stiffness or soreness in your Achilles tendon when you first wake up
Your doctor may require imaging tests to ensure whether you are suffering from Achilles tendinitis. It may include x-rays, MRI scans, or ultrasounds.
Causes
What Is the Achilles Tendon?
Of all the tendons in your body, the largest, strongest, and most important one is the Achilles tendon. The Achilles tendon is responsible for the movement of your foot, toes, ankle, heel, and calf. It absorbs the force from bearing weight. While the Achilles does a lot for you, it’s vulnerable to injuries and poor blood supply.
What Causes Achilles Tendinitis?
The development of Achilles tendinitis is often due to the amount of strain it faces, which can be caused or contributed by:
- A high or sudden increase in physical activity, such as sports, running, and ballet
- Activities that require quick stops and changes in direction
- Exercising without warming up beforehand
- A lack of physical activity where the tendon has to work harder to make up for the weakened lower leg muscles
- Obesity: The increase in body weight might put too much pressure on the Achilles tendon and makes it more prone to injuries
- Joint disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis
- Biomechanical abnormalities
- Wearing ill-fitting shoes
If left untreated, tendinitis can lead to a more chronic condition called Achilles tendinosis. The condition involves the non-inflammatory degeneration of the tendon which leads to thickening of the tendon and scar tissue formation. In some cases, if there is enough trauma to the affected area, it can lead to a tendon rupture.
Scheduling a diagnostic assessment with our practice can determine whether or not you are dealing with this condition.
Treatment
What Are the Treatments for Achilles Tendinitis?
Treating the issue of Achilles Tendinitis early on is crucial in reducing the risk of future complications.
Some treatments may include:
- Strengthening and stretching exercises. These types of exercises can be quick, easy, and accessible. Doing a few minutes of stretching exercise while you’re sitting on the couch or watching TV can do a lot for you if you are in recovery or preventing Achilles tendinitis.
- Steadily decrease your activities; continuing exercises like running or playing any sports is never a good idea if you’re dealing with this condition.
- Custom orthotics can elevate your heel and add some relief to the strain placed on your Achilles tendon.
- Over-the-counter insoles can increase the amount of cushioning needed under your heel. Orthotics can support the tendon by absorbing the amount of pressure placed on it by walking.
- Shockwave therapy is a non-invasive treatment that delivers high-energy sound wave pulses to the affected area of the Achilles. The waves trigger your natural healing response to repair the damage done to the Achilles tendon and reduce pain.
- Using anti-inflammatory medicine, such as ibuprofen or aspirin will reduce pain and swelling.
- In some cases, physical therapy may be necessary.
The RICE Method
An effective mode of treatment for Achilles tendinitis is the RICE method, also known as rest, ice, compression, and elevation:
- Rest. Make sure you don’t put any pressure or weight on the affected area for at least 1 to 2 days until you find that you’re walking without pain.
- Ice. Apply ice or an ice pack against the tendon for about 20 minutes, which should make the swelling go down quicker.
- Compression. Wrap the affected area with a bandage or athletic tape and compress the tendon. It will help in preventing any more swelling. However, make sure you aren’t wrapping too tightly.
- Elevation. Keeping your foot elevated above the chest level will aid in lowering the swelling.
Surgery
If home treatments aren’t working, your doctor may recommend a few options to repair the Achilles tendon:
- Lengthening the calf muscles
- Repairing the tendons
- Removing bone spurs
- Strengthening the affected area by moving another tendon to the heel bone
Risk Factors
- Running/exercising in ill-fitted or worn-out sneakers
- Wearing shoes with high heels
- High impact sports
- Lack of physical activity
- Obesity
- Joint disorders
- Biomechanical abnormalities
- Flat feet
- High arches
- Tight calf muscles
Prevention
How To Prevent Achilles Tendinitis
There are numerous amounts of actions you can take if you fear that you may develop Achilles tendinitis:
- Stretch and strengthen the area with small exercises.
- Warm up before exercising or any physical activities.
- Combine high and low-impact exercises, such as swimming or basketball.
- Exercise on flat/even surfaces.
- Replace any worn-out running shoes.
- Avoid wearing high-heeled shoes.
- Get custom orthotics, as they can alleviate the stress and strain on your tendon.
Whether you do or don’t have Achilles tendinitis, it can be a good idea to look into the services of our skilled foot specialists. Your overall health is essential. Get the best comfort you can find with our products today!